QUESTIONS:
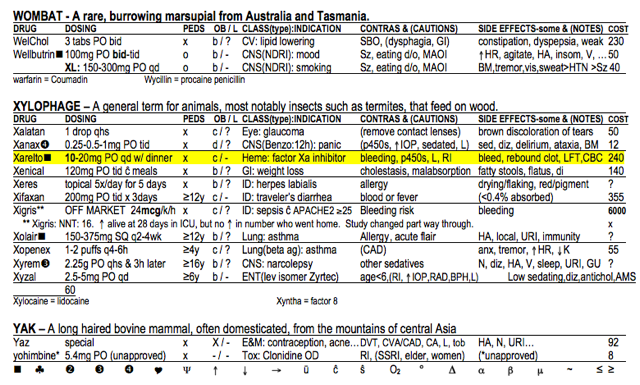
- You are asked to send a pregnant with a small DVT home on Xarelto. How does Xarelto work? Does it have a black box warning? Is it safe in pregnancy? What medical conditions require caution when using Xarelto?
- You have a patient who has had a bad headache for 3 weeks and came to the ED because neither her doctor nor her neurologist can figure out the cause. You astutely ask if she has started any new medications recently. She tells you she started Prevacid about a month ago. Can Prevacid cause a headache? What medications are most likely to cause headache?
- You have a patient with pancreatitis, but no alcohol use, gallstones or recent scorpion stings. Medications are the third most common cause of pancreatitis, what medications are on the list?
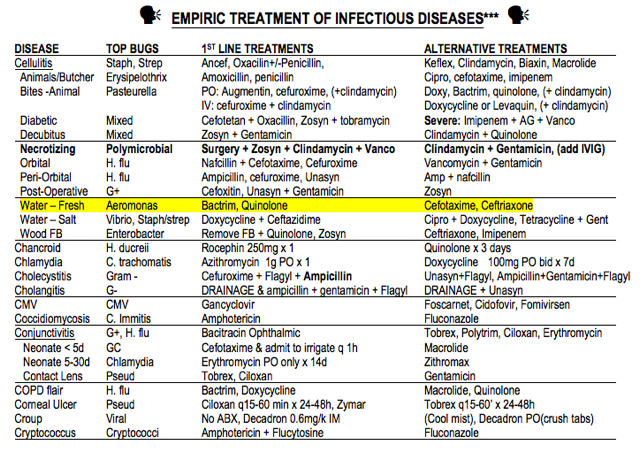
- You have a patient who recently cut his foot on wood in a fresh water lake and now has cellulitis. His doctor started him on Keflex, but it is not working and now he is worse. What organism(s) do you need to cover? What antimicrobial(s) should you start? What are alternate agents you could chose?
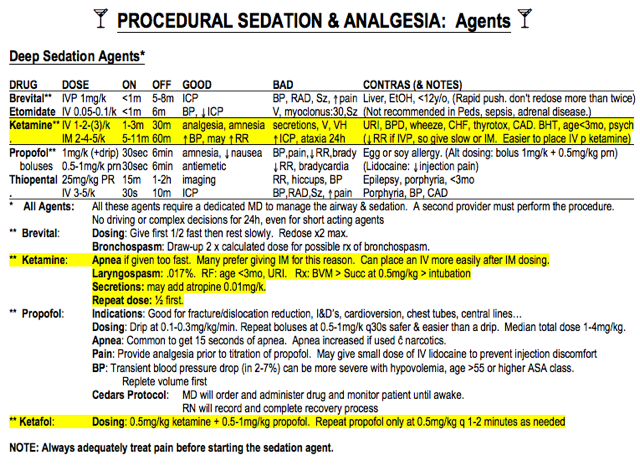
- You have a pediatric patient that you are going to perform procedural sedation on for fracture reduction. You decide to use ketamine, but want to refresh your memory on its use. What is the recommended dose for ketamine? What are contraindications to it’s use? How long should you expect it to last?
***********************************************************
ANWERS:
- Xarelto is a factor Xa inhibitor, it has a black box warning. The “c” is the safety class in pregnancy, which is usually considered safe. The contraindication section has “L and RI” listed letting you know that this drug should be avoided if there is significant liver disease or renal insufficiency.
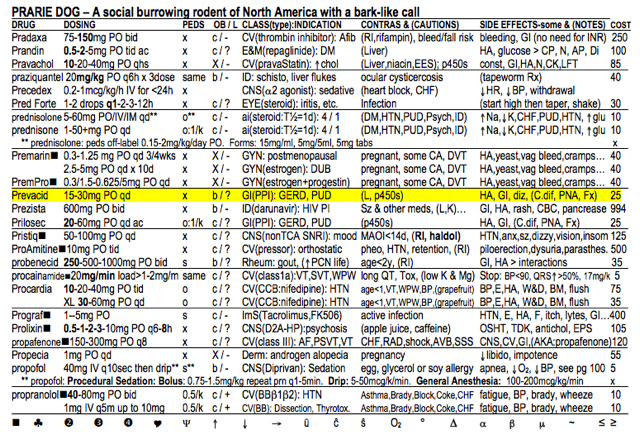
2. Prevacid: Look at the side effect column on the right side and notice HA (headache) is the first side effect listed. You stop the Prevacid and replace it with Zantac.
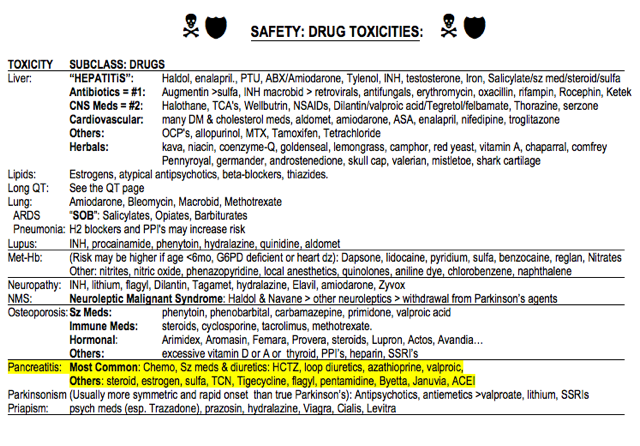
3. Pancreatitis: The drug toxicity section of the book has “pancreatitis”
- Most Common: chemo, seizure meds, diuretics, azathioprine, valproic acid.
- Others: steroids, estrogen, sulfas, doxycycline, Tigecycline, Flagyl, pentamidine, Byetta, Januvia, ACE inhibitors
4. Cellulitis from a lake: go to the empiric antibiotic section of the book and look up cellulitis and then “Water – fresh” and see that you need to cover Aeromonas and first line treatment is Bactrim or a quinolone and other options are cefotaxime or ceftriaxone
5. Ketamine: go to the procedural sedation section of the book. The dose is 1-2mg/kg IV or 2-4mg/kg IM. Relative contraindications include URI, wheeing, coronary disease, CHF, thyrotoxicosis, psychosis or age < 3 months. Duration of action is ~30 minutes for IV use and ~60 minutes for IM use.
****

Very good source