History of Present Illness:
A man in his early-40’s with a history of bradycardia presents to the hospital with sudden onset pleuritic chest pain on the left side
Vital Signs & Physical Exam:
Vital signs are normal except for a pulse in the 40s. Physical exam is otherwise normal except for pain with range of motion and decreased range of motion
Initial Diagnostic Testing: see EKG and CXR below
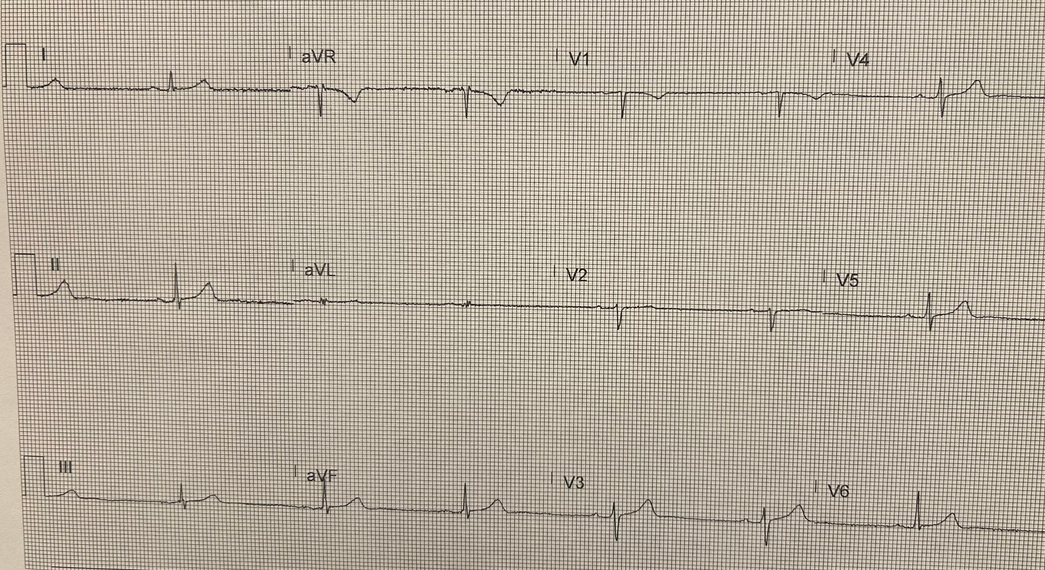
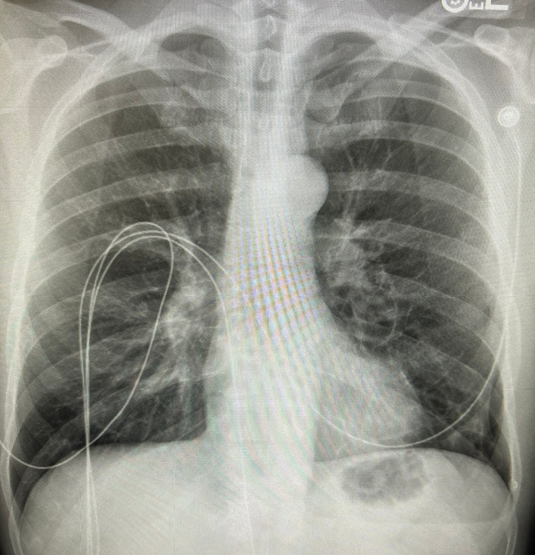
What is the most likely diagnosis?
- A) PE
- B) Pericarditis
- C) Pneumothorax
- D) Aortic dissection
SCROLL DOWN FOR ANSWERS & 1-MINUTE CONSULT
<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<< ADVERTISEMENT & SPACER >>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>
****************************************************************************
THE EMERGENCY MEDICINE POCKETBOOK TRIFECTA

Emergency Medicine 1-Minute Consult, 5th edition
A-to-Z EM Pharmacopoeia & Antibiotic Guide, 5th edition
8-in-1 Emergency Department Quick Reference, 5th edition
******************************************************************************
***************************************************************************
<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<< END SPACER >>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>
ANSWER: What is the most likely diagnosis?
- A) PE
- B) Pericarditis
- C) Pneumothorax – CORRECT – XR shows a left basilar PTX. Always look at image yourself when worried about PTX
- D) Aortic dissection – can’t rule out with CXR but it looks very normal. Always look at image yourself when worried about AD
OUTCOME: PTX stable on repeat x-ray. CT surg consulted. Sent home with f/u. H/o prior PTX with pleurodesis
PNEUMOTHORAX: (See TRAUMA chapter for traumatic)
Clinical: Pleuritic chest pain >DOE >SOB at rest >hypoxia >hypotension
Causes: Primary: no known lung disease and age <50y. Usually a 20-40y/o svelte smoker.
Secondary: trauma, COPD, cystic fibrosis, PCP, TB, CA, endometriosis (catamenial)
Catamenia: w/in 72h before/after start of menses; often right-sided w/ pleural lesions
Testing: Sensitivities: XR: 80% (must look for it carefully, supine CXR much worse), CT:100%
Size: Small (<15%): <1cm lateral & <3cm at apex. Large (>15%): >1cm lateral & >3cm apex
EKG: If left-sided may show low voltages in lateral and precordial leads
Treatment: Varies depending on cause, size, duration and if recurrent
If PTX >2d old, re-expand w/o suction to prevent Re-Expansion Pulmonary Edema
Primary: Small: <3cm from inner rib to apex: O2 x 6h, home w/ 24 & 48h f/u if no after 6h obs
Large: Aspirate àshut valve, 4h CXR: if nl remove cath & CXR in 2h, if +PTX then Heimlich
If >2.5L aspirated, air leak likely so chest tube and admit to ICU
ACI: Stop smoking, 24 & 48h f/u: reabsorb about 1%/day, no air travel or ascent to altitude
Recurrent: if second episode needs to see surgeon for possible pleurodesis or stapling
Secondary: If age >50 likely secondary. Chest tube (because usually have air leak) & admit to ICU
Refractory: stapling, abrasion or pleurodesis to prevent recurrences
